Difference between revisions of "GAUPS 1.0 Instructions"
m |
|||
| (20 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Open Source == | == Open Source == | ||
| − | GAUPS is derived from Bart Dring's open-source [http://buildlog.net/ Buildlog.net] Arduino-compatible Stepper Motor Driver Shield rev 3. | + | GAUPS is derived from Bart Dring's open-source [http://buildlog.net/ Buildlog.net] Arduino-compatible Stepper Motor Driver Shield rev 3. Thank you, Bart! |
| − | GAUPS is open-source hardware, released under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 License. | + | GAUPS is open-source hardware, released under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 License. KiCAD files will be available here soon. |
== Assembly == | == Assembly == | ||
| − | It's easiest to assemble the board in the order of component height, leaving the tallest last. | + | It's easiest to assemble the board in the order of component height, leaving the tallest last. For the parts with long leads, trim them as soon as you've soldered them (do not trim the Arduino headers, obviously). The instructions assume the board is held with the driver labels ("X AXIS" etc) the right way up, as shown. |
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
|rowspan="2" | [[File:GAUPS_1.0_Assembly_01_R1.jpg|450px]] | |rowspan="2" | [[File:GAUPS_1.0_Assembly_01_R1.jpg|450px]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |Solder R1 (10 kΩ resistor). | + | |Solder R1 (10 kΩ resistor). Color code: [[File:Ra.png|link=]][[File:Rb1.png|link=]][[File:Rc.png|link=]][[File:Rd0.png|link=]][[File:Re.png|link=]][[File:Rd0.png|link=]][[File:Re.png|link=]][[File:Rd2.png|link=]][[File:Rf.png|link=]][[File:Rb1.png|link=]][[File:Rg.png|link=]] (1%) or [[File:Ra.png|link=]][[File:Rb1.png|link=]][[File:Rc.png|link=]][[File:Rd0.png|link=]][[File:Re.png|link=]][[File:Rd3.png|link=]][[File:Rf.png|link=]][[File:RbG.png|link=]][[File:Rg.png|link=]] (5%). |
|- | |- | ||
!rowspan="2" | 2 | !rowspan="2" | 2 | ||
| Line 43: | Line 43: | ||
|rowspan="2" | [[File:GAUPS_1.0_Assembly_05_C5-C8.jpg|450px]] | |rowspan="2" | [[File:GAUPS_1.0_Assembly_05_C5-C8.jpg|450px]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |Solder C5, C6, C7, C8 (100 nF capacitors). | + | |Solder C5, C6, C7, C8 (100 nF capacitors). These are not polarized, so orientation doesn't matter. |
|- | |- | ||
!rowspan="2" | 6 | !rowspan="2" | 6 | ||
| Line 73: | Line 73: | ||
|rowspan="2" | [[File:GAUPS_1.0_Assembly_10_JP1_DY_jumpers.jpg|450px]] | |rowspan="2" | [[File:GAUPS_1.0_Assembly_10_JP1_DY_jumpers.jpg|450px]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |Install two jumpers on JP1, either in the DY position (shown) or the A position (not shown). See [[#Jumper Settings|jumper settings]] below. Check all the soldering, remove any loose bits of solder, insert into the Arduino Uno, and you're done! | + | |Install two jumpers on JP1, either in the DY position (shown) or the A position (not shown). See [[#Jumper Settings|jumper settings]] below. Please note the orientation of the jumpers: they're vertical. Check all the soldering, remove any loose bits of solder, insert into the Arduino Uno, and you're done! |
|} | |} | ||
== Driver Orientation == | == Driver Orientation == | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Please pay attention to driver orientation!''' A driver inserted backwards will be destroyed instantly when the power is turned on. | ||
Driver pin VMOT (motor supply voltage) is marked with an arrow on the silkscreen (please note that this is different from the beta version). The motor outputs (1A, 1B, 2A, 2B) face the respective screw terminals. The electrolytic capacitor is near the VMOT pin, and the yellow ceramic capacitor is near the VDD pin. The digital inputs are toward the middle of the board. | Driver pin VMOT (motor supply voltage) is marked with an arrow on the silkscreen (please note that this is different from the beta version). The motor outputs (1A, 1B, 2A, 2B) face the respective screw terminals. The electrolytic capacitor is near the VMOT pin, and the yellow ceramic capacitor is near the VDD pin. The digital inputs are toward the middle of the board. | ||
| Line 107: | Line 109: | ||
!• | !• | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | Note that, in either case, the jumpers are vertical (parallel to the short edge of the board). | ||
== Switch Settings == | == Switch Settings == | ||
| Line 119: | Line 123: | ||
|- | |- | ||
!colspan="4"|SW1 switch | !colspan="4"|SW1 switch | ||
| − | + | | | |
| − | !colspan=" | + | !colspan="5"|''A4988 and DRV8825'' |
!''A4988'' | !''A4988'' | ||
!colspan="2"|''DRV8825'' | !colspan="2"|''DRV8825'' | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | !colspan="5"|''DRV8834'' | ||
|- | |- | ||
!X axis | !X axis | ||
| Line 128: | Line 134: | ||
!Z axis | !Z axis | ||
!A axis | !A axis | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | !Pin name | ||
!1 × | !1 × | ||
!2 × | !2 × | ||
| Line 133: | Line 141: | ||
!8 × | !8 × | ||
!16 × | !16 × | ||
| + | !16 × | ||
| + | !32 × | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | !Pin name | ||
| + | !2 × | ||
| + | !4 × | ||
!16 × | !16 × | ||
!32 × | !32 × | ||
| Line 140: | Line 154: | ||
!7 | !7 | ||
!1 | !1 | ||
| + | | | ||
!''MS1'' | !''MS1'' | ||
|OFF | |OFF | ||
| Line 148: | Line 163: | ||
|OFF | |OFF | ||
| ON | | ON | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | !''M0'' | ||
| + | | ON | ||
| + | |OFF | ||
| + | | ON | ||
| + | |OFF | ||
|- | |- | ||
!11 | !11 | ||
| Line 153: | Line 174: | ||
!8 | !8 | ||
!2 | !2 | ||
| + | | | ||
!''MS2'' | !''MS2'' | ||
|OFF | |OFF | ||
| Line 160: | Line 182: | ||
| ON | | ON | ||
|OFF | |OFF | ||
| + | | ON | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | !''M1'' | ||
| + | |OFF | ||
| + | |OFF | ||
| + | | ON | ||
| ON | | ON | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 166: | Line 194: | ||
!9 | !9 | ||
!3 | !3 | ||
| + | | | ||
!''MS3'' | !''MS3'' | ||
|OFF | |OFF | ||
| Line 174: | Line 203: | ||
| ON | | ON | ||
| ON | | ON | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | !''(CFG)'' | ||
| + | |colspan="4" align="center"|''not used'' | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | For instance, to set a DRV8825 driver on the Z axis to 8 × microstepping, | + | For instance, to set a DRV8825 driver on the Z axis to 8 × microstepping, |
set switches 7 on, 8 on, 9 off. In the Dual Y configuration, it's simplest to | set switches 7 on, 8 on, 9 off. In the Dual Y configuration, it's simplest to | ||
use the same type of driver and motor for both the Y axes (Y and A), and use | use the same type of driver and motor for both the Y axes (Y and A), and use | ||
the same microstepping configuration for both (switches 1–3 same as switches 4–6). | the same microstepping configuration for both (switches 1–3 same as switches 4–6). | ||
| + | |||
| + | Note that it is not possible to select all microstepping combinations for the DRV8834 | ||
| + | low-voltage stepper motor driver (1 × and 8 × would require pin | ||
| + | M0 to be held low). | ||
| + | |||
| + | === gShield/grblShield Compatibility === | ||
| + | |||
| + | To make a GAUPS behave exactly like a gShield (or an older grblShield with the Z-axis hack), | ||
| + | so that one can use the same settings for GRBL, set X and Y to 8 × microstepping, | ||
| + | and Z to 2 ×: | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | !1 | ||
| + | | ON | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | !2 | ||
| + | | ON | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | !3 | ||
| + | |OFF | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | !4 | ||
| + | | ON | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | !5 | ||
| + | | ON | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | !6 | ||
| + | |OFF | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | !7 | ||
| + | | ON | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | !8 | ||
| + | |OFF | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | !9 | ||
| + | |OFF | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | !10 | ||
| + | | ON | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | !11 | ||
| + | | ON | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | !12 | ||
| + | |OFF | ||
| + | |} | ||
== Connections == | == Connections == | ||
| Line 187: | Line 268: | ||
The motor power supply input is P5, the two bottom screw terminals in the block of ten on the left side of the board. Positive is next to the X axis motor terminals, negative at the bottom edge of the board. Please note that this is different from the beta version. The polarity is marked on the silkscreen on the back of the board (there was no room on the front). | The motor power supply input is P5, the two bottom screw terminals in the block of ten on the left side of the board. Positive is next to the X axis motor terminals, negative at the bottom edge of the board. Please note that this is different from the beta version. The polarity is marked on the silkscreen on the back of the board (there was no room on the front). | ||
| − | Do not make or break any connections while the board or the Arduino are powered. There is a high risk of destroying the drivers and/or the Arduino. | + | '''Do not make or break any connections while the board or the Arduino are powered.''' There is a high risk of destroying the drivers and/or the Arduino. |
[[File:GAUPS 1.0 Example Wiring.jpg|none|600px|thumb|GAUPS 1.0 Example Configuration]] | [[File:GAUPS 1.0 Example Wiring.jpg|none|600px|thumb|GAUPS 1.0 Example Configuration]] | ||
| Line 229: | Line 310: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | This is the standard direction of travel for a dual-motor dual-Y drive | + | This is the standard direction of travel for a dual-motor dual-Y drive eShapeoko |
| − | with any of the standard | + | with any of the standard eShapeoko belt configurations (teeth down, belt going |
under the idler wheels and over the belt pulley). This is also valid for a | under the idler wheels and over the belt pulley). This is also valid for a | ||
Shapeoko with any of the belt mods that have the belt facing teeth down. For | Shapeoko with any of the belt mods that have the belt facing teeth down. For | ||
| Line 249: | Line 330: | ||
in the opposite direction, too, and the direction can also be changed in firmware. | in the opposite direction, too, and the direction can also be changed in firmware. | ||
| − | == | + | == Power Supply == |
| + | |||
| + | The choice of voltage depends on the driver modules. The kit of parts, as | ||
| + | supplied, has capacitors rated at 35 V, so that's the maximum voltage. However, | ||
| + | the capacitors can be replaced. | ||
| + | |||
| + | With A4988 drivers, the maximum voltage is 35 V, but EMF induced in the motor | ||
| + | during braking can raise the supply voltage, so we do not recommend using more | ||
| + | than 30 V. The DRV8825 drivers are rated to 45 V, but, for the same reason, | ||
| + | we do not recommend more than 40 V (provided that the capacitors on the GAUPS | ||
| + | have been replaced with ones rated 50 V or more). | ||
| + | |||
| + | A4988 and DRV8825 both work from 12 V, but the most popular voltage for them | ||
| + | is 24 V. 19 V is also popular, because it's the typical voltage of a laptop | ||
| + | power supply, and many people have one of those lying around. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The DRV8834 driver operates from 2.5 V to 10.8 V, so it's ideal for low-voltage | ||
| + | applications. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Part List == | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| Line 279: | Line 379: | ||
|C5–C8 | |C5–C8 | ||
|4 | |4 | ||
| − | |Ceramic capacitor, 100 nF 50 V, 0.2" lead spacing | + | |Ceramic capacitor, 100 nF 50 V, X7R dielectric, 0.2" lead spacing |
|Multicomp | |Multicomp | ||
| − | | | + | |MCRR50104X7RK0050 |
|- | |- | ||
|SW1 | |SW1 | ||
| Line 343: | Line 443: | ||
with an asterisk are generic equivalents). This is especially important for the long-life | with an asterisk are generic equivalents). This is especially important for the long-life | ||
electrolytic capacitors of the correct form factor, and for the good quality screw terminals. | electrolytic capacitors of the correct form factor, and for the good quality screw terminals. | ||
| − | Also important | + | Also important are the long (15 mm pins) Arduino headers; the typical Arduino headers with |
| − | 10–12 mm pins | + | 10–12 mm pins are not tall enough for the solder joints on the back of the shield to |
clear the Arduino USB connector, and insulation is required. | clear the Arduino USB connector, and insulation is required. | ||
We reserve the right to substitute parts without notice. | We reserve the right to substitute parts without notice. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Schematic == | ||
| + | [[File:GAUPS 1.0 schematic.png|900px]] | ||
Latest revision as of 23:35, 19 April 2017
Open Source
GAUPS is derived from Bart Dring's open-source Buildlog.net Arduino-compatible Stepper Motor Driver Shield rev 3. Thank you, Bart!
GAUPS is open-source hardware, released under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 License. KiCAD files will be available here soon.
Assembly
It's easiest to assemble the board in the order of component height, leaving the tallest last. For the parts with long leads, trim them as soon as you've soldered them (do not trim the Arduino headers, obviously). The instructions assume the board is held with the driver labels ("X AXIS" etc) the right way up, as shown.
| Step | Part Image and Instructions | Board Image |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 
| |
| Solder R1 (10 kΩ resistor). Color code: | ||
| 2 | 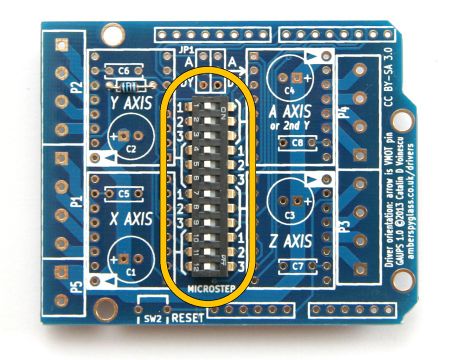
| |
| Solder SW1 (12-way DIP switch). Orient it numbers to the left, "ON" text in the upper-right corner. The 1, 2 and 3 labels will match the 1, 2 and 3 silkscreen labels for the A axis. | ||
| 3 | 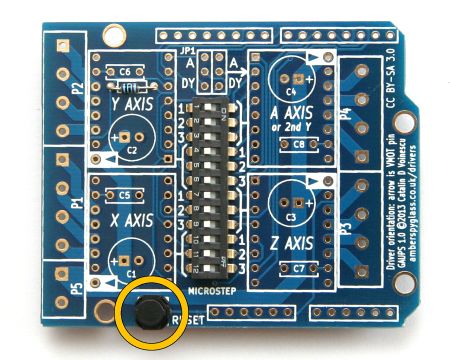
| |
| Solder SW2 (push-button), taking care not to overheat it. | ||
| 4 | 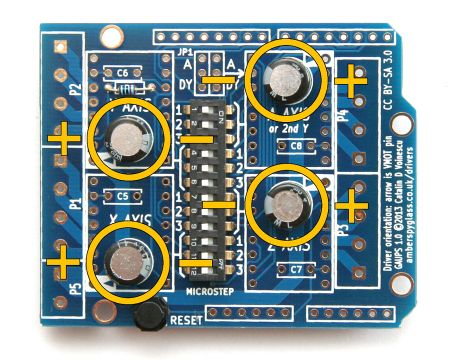
| |
| Solder C1, C2, C3, C4 (47 µF 35 V capacitors), paying attention to the orientation. Install with the negative terminal (shorter lead, marked with a stripe on the body of the capacitor) toward the middle of the board. | ||
| 5 | 
| |
| Solder C5, C6, C7, C8 (100 nF capacitors). These are not polarized, so orientation doesn't matter. | ||
| 6 | 
| |
| Solder the eight 8-way female headers for the drivers. | ||
| 7 | 
| |
| Solder JP1 (2×3-pin male header). The holes for it are very tight (sorry!). The best way is to push it in with a flat, rigid object. | ||
| 8 | 
| |
| Solder the two 6-way and two 8-way Arduino stacking headers, taking care to not to deposit solder on the long pins (except where they meet the PCB, of course). Make sure the pins are straight and parallel before soldering them. | ||
| 9 |    
|

|
| Join one 2-way and two 4-way screw terminals, by sliding the little dovetails into the slots. Solder them as P5, P1 and P2, with the openings for the wires toward the outside of the board. Join the remaining two 4-way screw terminals. Solder them as P3 and P4. | ||
| 10 | 
| |
| Install two jumpers on JP1, either in the DY position (shown) or the A position (not shown). See jumper settings below. Please note the orientation of the jumpers: they're vertical. Check all the soldering, remove any loose bits of solder, insert into the Arduino Uno, and you're done! |
Driver Orientation
Please pay attention to driver orientation! A driver inserted backwards will be destroyed instantly when the power is turned on.
Driver pin VMOT (motor supply voltage) is marked with an arrow on the silkscreen (please note that this is different from the beta version). The motor outputs (1A, 1B, 2A, 2B) face the respective screw terminals. The electrolytic capacitor is near the VMOT pin, and the yellow ceramic capacitor is near the VDD pin. The digital inputs are toward the middle of the board.
Note that two drivers (X and Y) are oriented one way, the other two (Z and A) the other way.
Jumper Settings
For Dual-Y operation, the A driver takes the same control signals (STEP and DIR) as the Y driver, acting as a second Y driver instead of a fourth independent axis. Install two jumpers in the positions marked 'DY' on the board.
For 4-axis operation (or spindle relay in the A axis slot, instead of a driver), STEP and DIR for the A driver come from Arduino pins D12 and D13. Install two jumpers in the positions marked 'A' on the board.
| JP1 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dual-Y | 4 axes | |||
| • | • | • • |
• • | |
| • • |
• • | |||
| • | • | |||
Note that, in either case, the jumpers are vertical (parallel to the short edge of the board).
Switch Settings
DIP switches are OFF to the left (the side of the switch with the numbers), ON to the right (the side labelled "ON").
Microstepping is controlled independently for each of the four drivers. Each driver has three switches associated with it. The silkscreen shows which switches apply to which driver.
| SW1 switch | A4988 and DRV8825 | A4988 | DRV8825 | DRV8834 | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X axis | Y axis | Z axis | A axis | Pin name | 1 × | 2 × | 4 × | 8 × | 16 × | 16 × | 32 × | Pin name | 2 × | 4 × | 16 × | 32 × | ||
| 10 | 4 | 7 | 1 | MS1 | OFF | ON | OFF | ON | ON | OFF | ON | M0 | ON | OFF | ON | OFF | ||
| 11 | 5 | 8 | 2 | MS2 | OFF | OFF | ON | ON | ON | OFF | ON | M1 | OFF | OFF | ON | ON | ||
| 12 | 6 | 9 | 3 | MS3 | OFF | OFF | OFF | OFF | ON | ON | ON | (CFG) | not used | |||||
For instance, to set a DRV8825 driver on the Z axis to 8 × microstepping, set switches 7 on, 8 on, 9 off. In the Dual Y configuration, it's simplest to use the same type of driver and motor for both the Y axes (Y and A), and use the same microstepping configuration for both (switches 1–3 same as switches 4–6).
Note that it is not possible to select all microstepping combinations for the DRV8834 low-voltage stepper motor driver (1 × and 8 × would require pin M0 to be held low).
gShield/grblShield Compatibility
To make a GAUPS behave exactly like a gShield (or an older grblShield with the Z-axis hack), so that one can use the same settings for GRBL, set X and Y to 8 × microstepping, and Z to 2 ×:
| 1 | ON |
|---|---|
| 2 | ON |
| 3 | OFF |
| 4 | ON |
| 5 | ON |
| 6 | OFF |
| 7 | ON |
| 8 | OFF |
| 9 | OFF |
| 10 | ON |
| 11 | ON |
| 12 | OFF |
Connections
The motor screw terminals are connected to the driver outputs nearest to them, in the same order.
The motor power supply input is P5, the two bottom screw terminals in the block of ten on the left side of the board. Positive is next to the X axis motor terminals, negative at the bottom edge of the board. Please note that this is different from the beta version. The polarity is marked on the silkscreen on the back of the board (there was no room on the front).
Do not make or break any connections while the board or the Arduino are powered. There is a high risk of destroying the drivers and/or the Arduino.
This image (click on it to enlarge) shows an example configuration:
- Four drivers and four motors
- Dual-Y (two Y motors, each with its own driver)
- 16 × microstepping on the X and Y axes
- Half-stepping (2 ×) on the Z axis
- Pololu A4988 green drivers (note that other driver modules may have the trimpot in a different location, so do not use it to decide the driver module orientation. Always check the pin labels).
Also, when using GRBL 0.8 or 0.9 with the "invert mask" set to 0, Pololu A4988 green or black drivers, and the motors we carry in our store, wired as shown, for a move in the positive direction of each axis, the motors turn as follows (as viewed looking into the shaft):
| Axis | Motor | Axis Positive Direction | Motor Direction |
|---|---|---|---|
| X | Right | Counter-clockwise | |
| Y | Left (Y driver) | Toward the back | Counter-clockwise |
| Right (A driver) | Clockwise | ||
| Z | Up | Clockwise |
This is the standard direction of travel for a dual-motor dual-Y drive eShapeoko with any of the standard eShapeoko belt configurations (teeth down, belt going under the idler wheels and over the belt pulley). This is also valid for a Shapeoko with any of the belt mods that have the belt facing teeth down. For the original Shapeoko configuration (belt teeth up, going over the idler wheels and under the belt pulley) and any other teeth up configuration, reverse the direction of X and Y motors (by reversing the connections, black–green–blue–red instead of red–blue–green–black).
Note that not all motors from all manufacturers turn in the same direction when wired the same, although this seems to be the most common case. If your motor has different color wires, always determine the correct pairing before wiring the motors, to avoid damage to the drivers. Any configuration will work, as long as the wires in each pair are next to each other (pins 1 and 2 one pair, pins 3 and 4 another pair).
Also note that driver modules other than Pololu A4988 may turn the motors in the opposite direction, too, and the direction can also be changed in firmware.
Power Supply
The choice of voltage depends on the driver modules. The kit of parts, as supplied, has capacitors rated at 35 V, so that's the maximum voltage. However, the capacitors can be replaced.
With A4988 drivers, the maximum voltage is 35 V, but EMF induced in the motor during braking can raise the supply voltage, so we do not recommend using more than 30 V. The DRV8825 drivers are rated to 45 V, but, for the same reason, we do not recommend more than 40 V (provided that the capacitors on the GAUPS have been replaced with ones rated 50 V or more).
A4988 and DRV8825 both work from 12 V, but the most popular voltage for them is 24 V. 19 V is also popular, because it's the typical voltage of a laptop power supply, and many people have one of those lying around.
The DRV8834 driver operates from 2.5 V to 10.8 V, so it's ideal for low-voltage applications.
Part List
| Part | Count | Description | Manufacturer | Part Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PCB | 1 | GAUPS 1.0 PCB, dual-side 1.6 mm FR4, through-plated, ENIG, RoHS | Amber Spyglass Ltd | — |
| R1 | 1 | Resistor, 10 kΩ 0.125 W, metal film | Multicomp | MF12 10K |
| C1–C4 | 4 | Aluminium electrolytic capacitor, 47 µF 35 V, long life (5000 hours @ 105°C), radial, 2.5 mm lead spacing, ∅ 8 mm, 5 mm tall |
Rubycon | 35ML47MEFC8X5 |
| C5–C8 | 4 | Ceramic capacitor, 100 nF 50 V, X7R dielectric, 0.2" lead spacing | Multicomp | MCRR50104X7RK0050 |
| SW1 | 1 | Low-profile 12-way DIP switch, 0.1" pitch, 0.3" wide | Multicomp * | MCEI-12 |
| SW2 | 1 | Tactile switch, 6 mm | Panasonic | EVQPVG05K |
| JP1 | 1 | 6-way dual-row male 0.1" pitch header, straight | AMP * | 826925-3 |
| Jumper | 2 | Jumper for 0.1" pitch header, blue | Harwin * | M7583-05 |
| U1–U4 | 8 | 8-way single-row female 0.1" pitch header, straight | Multicomp * | 2212S-08SG-85 |
| J1, J2 | 2 | 6-way single-row long pin (15 mm) female 0.1" pitch headers, straight | Samtec * | SSQ-106-04-F-S |
| J3, J4 | 2 | 8-way single-row long pin (15 mm) female 0.1" pitch headers, straight | Samtec * | SSQ-108-04-F-S |
| P1–P4 | 4 | 4-way side-entry PCB screw terminal, 5 mm pitch | Camden Boss | CTB5202/4 |
| P5 | 1 | 2-way side-entry PCB screw terminal, 5 mm pitch | Camden Boss | CTB5202/2 |
For most components, numerous equivalent parts exist from various manufacturers. The given manufacturers and part numbers are just examples of compatible parts. However, except where marked with an asterisk, the supplied parts in our kit are exactly those listed here (those with an asterisk are generic equivalents). This is especially important for the long-life electrolytic capacitors of the correct form factor, and for the good quality screw terminals. Also important are the long (15 mm pins) Arduino headers; the typical Arduino headers with 10–12 mm pins are not tall enough for the solder joints on the back of the shield to clear the Arduino USB connector, and insulation is required.
We reserve the right to substitute parts without notice.











